Stable Vs Unstable Angina Ecg

However unstable angina is considered an acute coronary syndrome because it is an imminent precursor to myocardial infarction.
Stable vs unstable angina ecg. Inferior wall ischemia infarction may cause pain located primarily in the epigastrium. 2015 esc guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent st segment elevation. The most common cause is reduced blood flow to the heart muscle because the coronary arteries are narrowed by fatty buildups atherosclerosis which can rupture causing injury to the coronary blood vessel resulting in blood clotting which blocks the flow of blood. Task force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent.
Roffi m patrono c collet jp et al. Note that all troponin assays regardless of their detection sensitivity do not rule out unstable angina or stable coronary ischemia clinical management decisions should not be based solely on troponin levels but on thorough investigation and risk assessment that includes detailed clinical assessment observation repeated ecg tests and where available functional testing. Unstable angina or sometimes referred to as acute coronary syndrome causes unexpected chest pain and usually occurs while resting. Unstable angina is an acute coronary syndrome that is defined by the absence of biochemical evidence of myocardial damage.
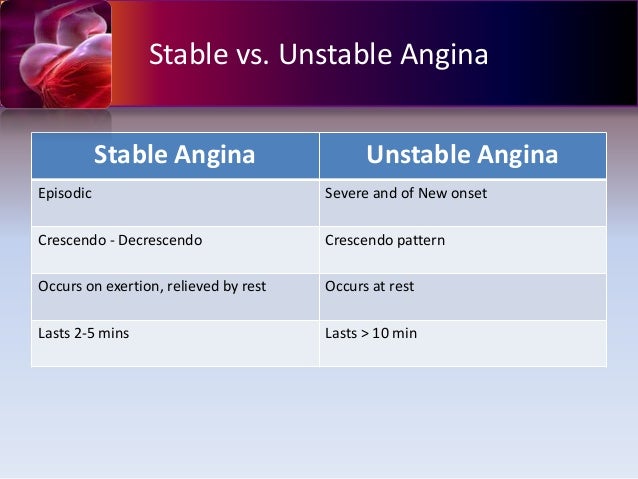
Stable angina occurs because the blood going to the heart muscle is not enough to cover for the extra workload in exercise. Physical examination as previously described is non specific. Angina that is increasing in frequency longer in duration or lower in threshold. Unstable angina differs from stable angina in that the discomfort is usually more intense and easily provoked and st segment depression or elevation on ecg may occur.
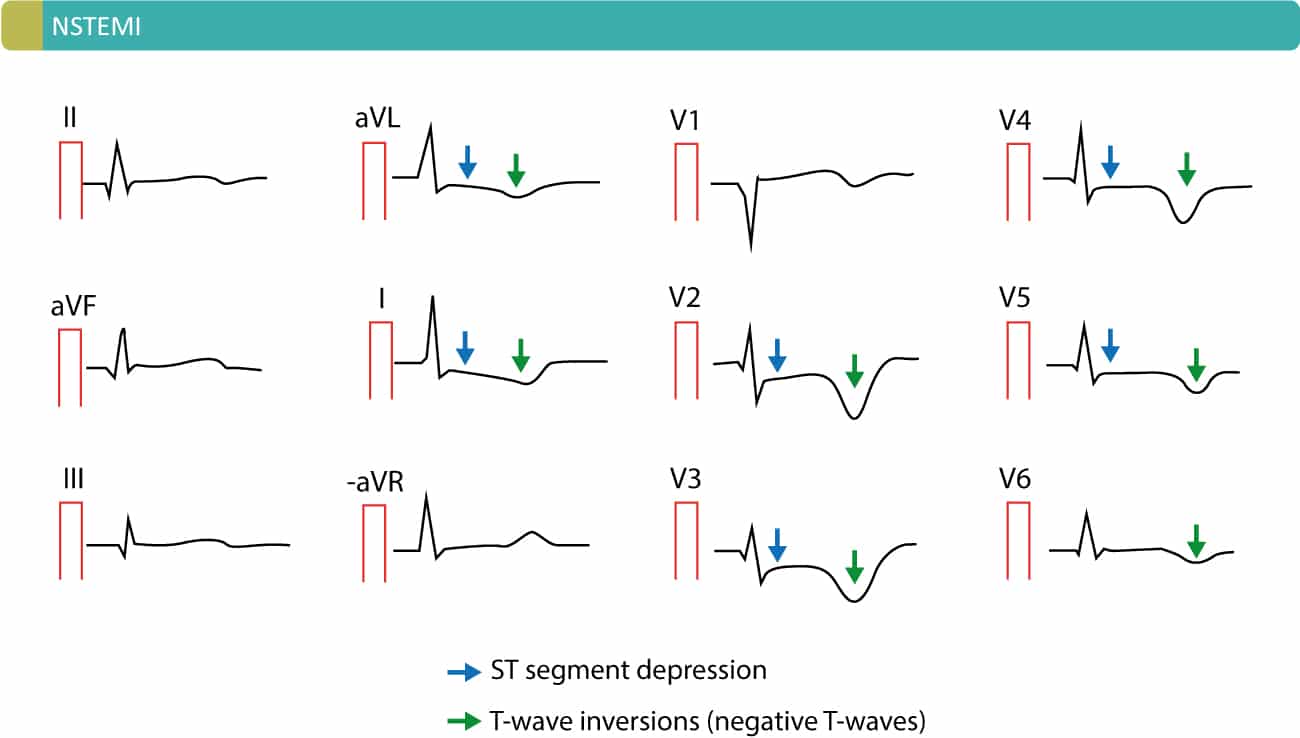
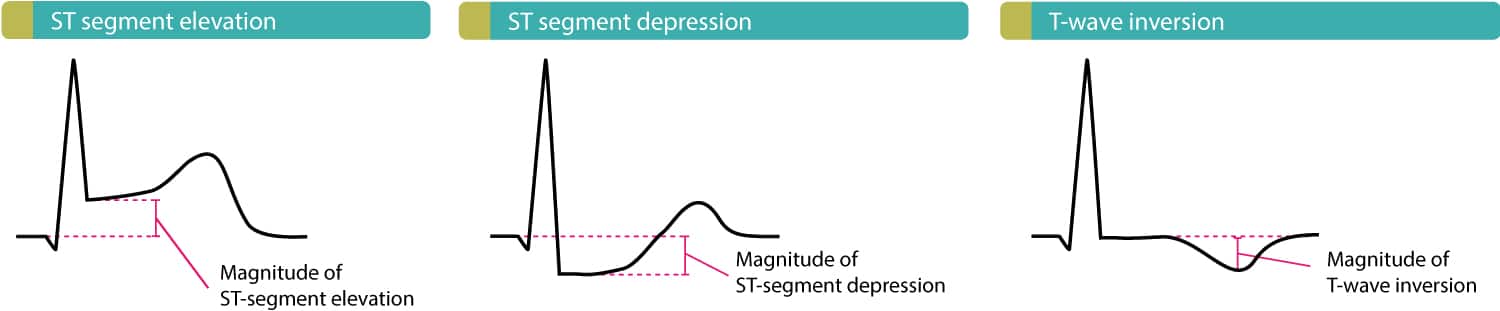
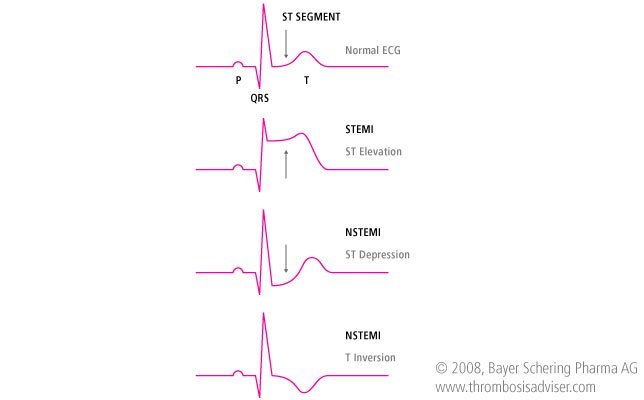
Unstable angina ua is an acute coronary syndrome that is defined by the absence of biochemical evidence of myocardial damage. The ecg frequently shows changes st segment depression and ischemic t wave but without changes in qrs. Definition of stable and unstable angina stable coronary artery disease angina pectoris in classical angina pectoris the pain is typically localized near the sternum. Pain may radiate to the back neck jaw or arms.
Unstable angina occurs because a blood clot blocks an artery supplying the heart muscle. Prolonged 20 minutes angina at rest. The diagnosis of unstable angina and non stemi is predominantly based on the ecg and cardiac enzymes. Approximately 50 of patients with unstable angina progress to myocardial infarction within 30 days if left untreated.
It is characterised by specific clinical findings of. Unstable angina is only diagnosed if there are no evidence of myocardial infarction necrosis. Stable vs unstable angina stable angina occurs with exertion while unstable angina comes on while the patient is at rest. Here is the comparison chart to show you the difference between stable and unstable angina.