Stable Vs Unstable Angina

An attack of unstable angina is an emergency and you should seek.
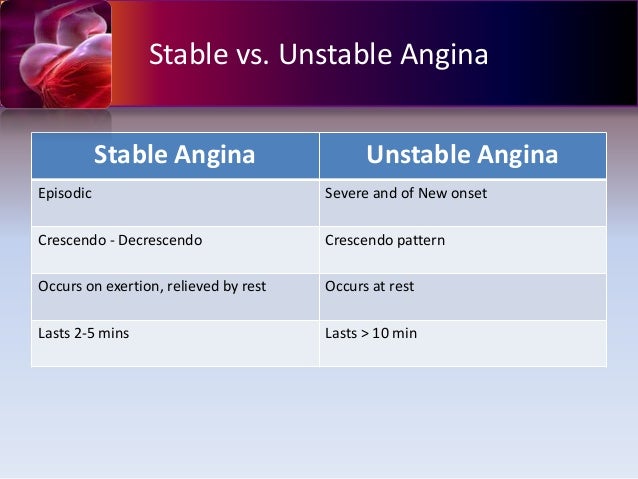
Stable vs unstable angina. The pain is the same every time and can be relieved by rest and medication. When you climb stairs exercise or walk your heart demands more blood but narrowed arteries slow down blood flow. Angina technically means chest or heart pain. Unstable angina is defined as having more frequent episodes of angina chest pain with less exertion having angina chest pain when resting or having new onset of severe angina.
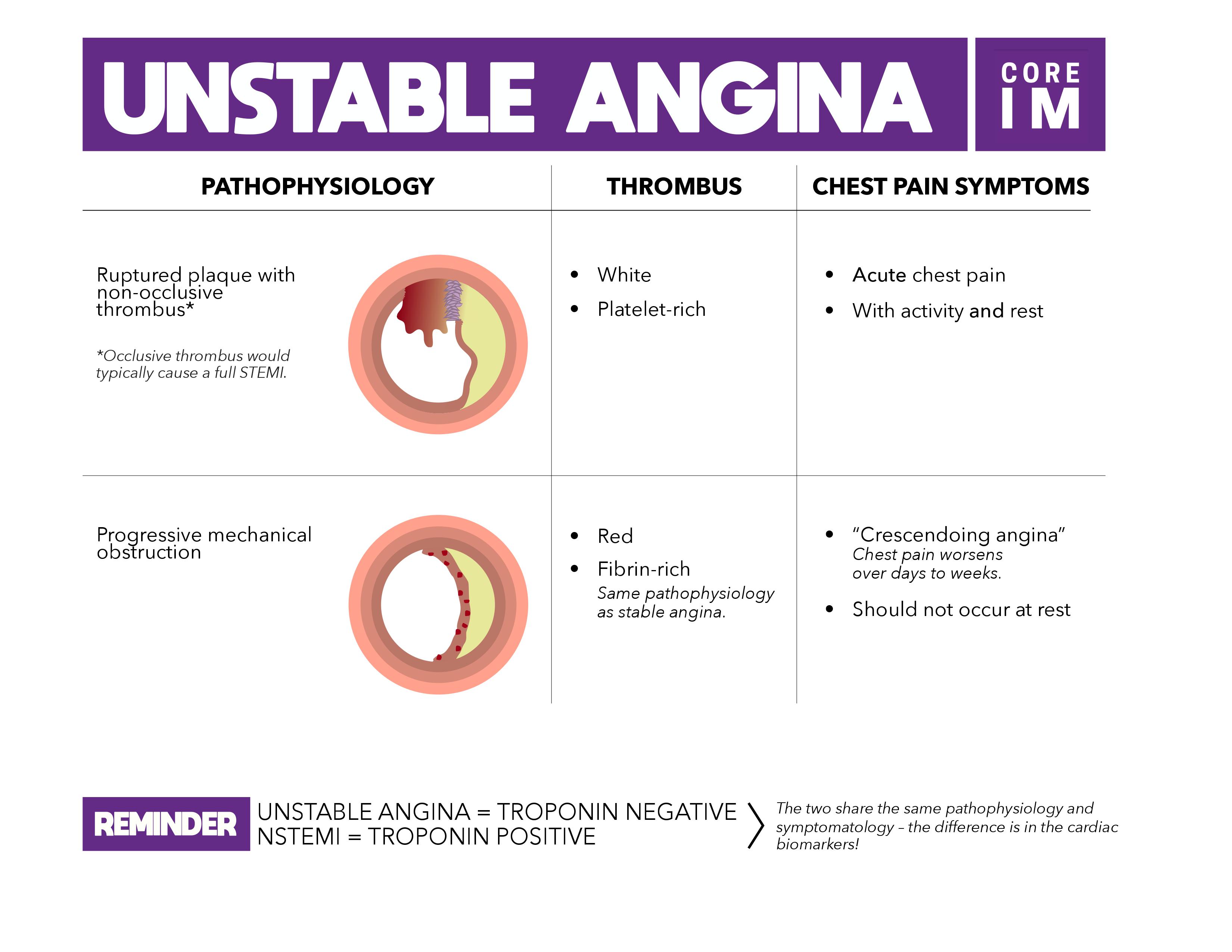
When dealing with stable and unstable angina what you have to keep in mind is that both are due to low oxygenation of the heart. Unstable angina means that blockages in the arteries supplying your heart with blood and oxygen have reached a critical level. Stable vs unstable angina stable angina occurs with exertion while unstable angina comes on while the patient is at rest. Stable angina has a pattern and occurs when the person physically active and the heart s workload is heavy.
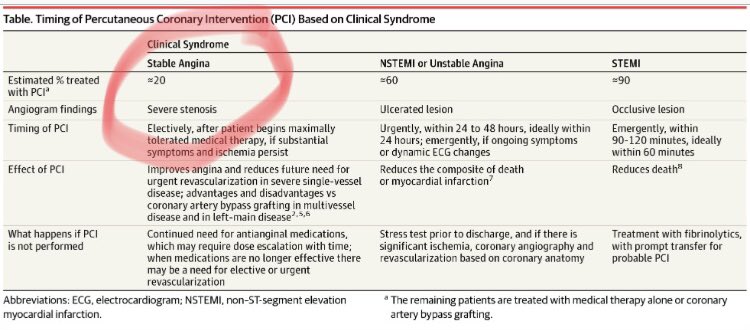
Patients who present with acute angina must be categorized as stable or unstable. Summary of stable vs unstable angina. Vasoconstriction versus vasodilation if a patient has coronary artery disease cad which is caused by high cholesterol there is increased plaque formation within. Stable angina occurs because the blood going to the heart muscle is not enough to cover for the extra workload in exercise.
Stable angina is chest discomfort shortness of breath or any of the symptoms described above that happens with a predictable reliable amount of exertion or stress and when that pattern has been present for more that four weeks. Although stable and unstable angina have similar symptoms they differ in terms of severity and when the symptoms occur. Unstable angina happens when the angina worsens. Angina is a type of chest pain resulting from reduced blood flow to the heart.
Stable angina is usually triggered by physical activity. This is stable angina. The angina is stable when the seizures appear in physical exertion or emotional stress for more than one month and there are no significant changes in the main features of the pain. Patients who have unstable angina should be further categorized as high intermediate or low risk table 1.










/unstable-angina-1745300-FINAL-bc6591effb28413082e53696e8636ae7.png)