Stable Vs Unstable Angina Pathophysiology

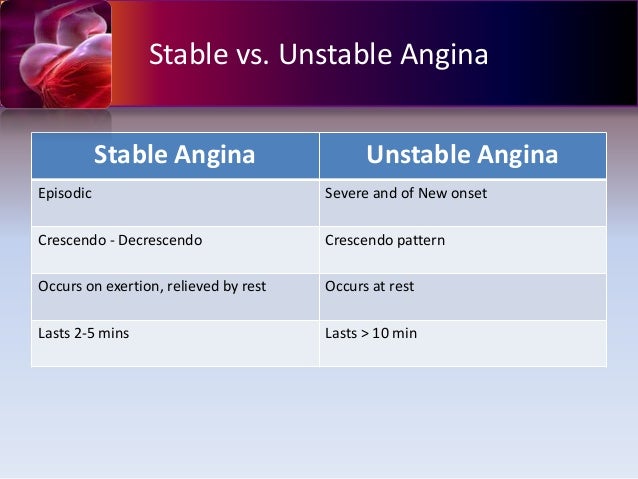
So just a reminder stable angina is relieved by rest while unstable angina still causes chest pain even during rest.
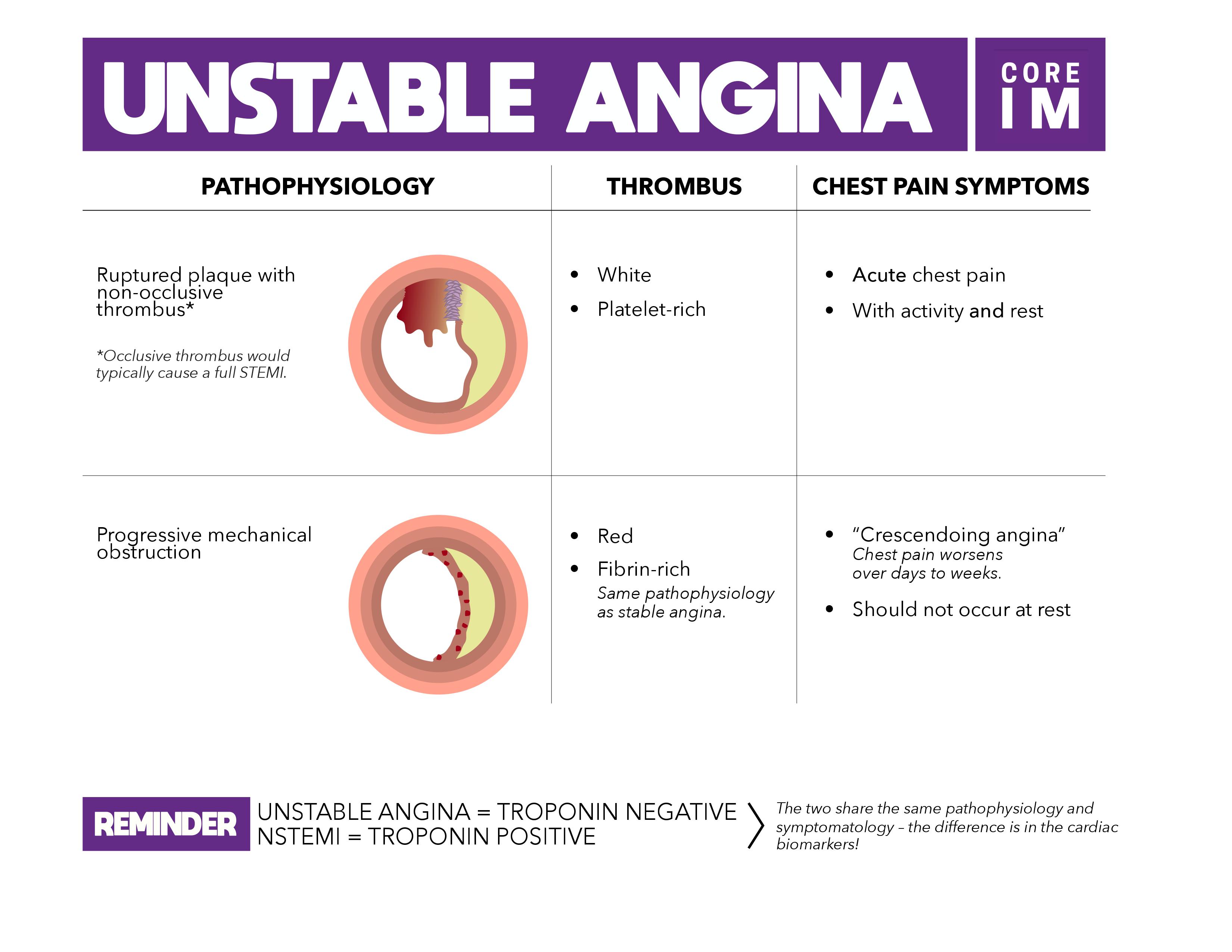
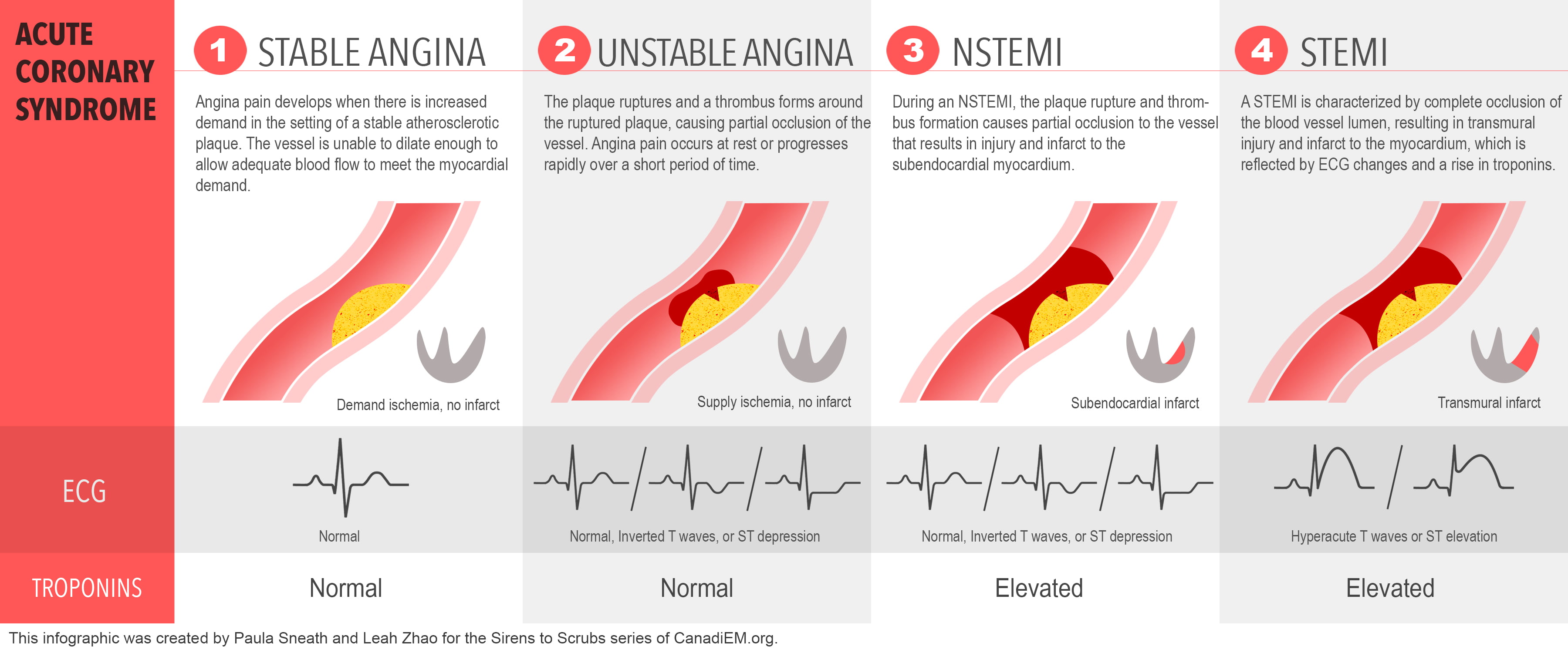
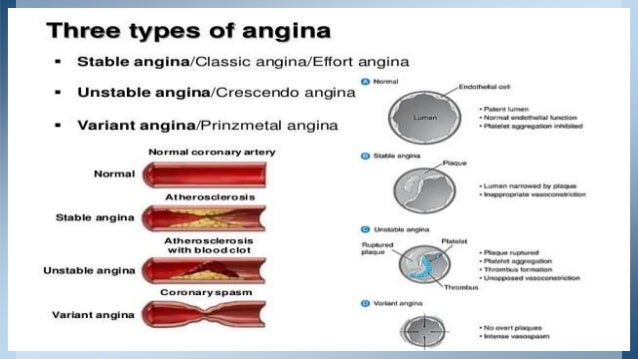
Stable vs unstable angina pathophysiology. Stable vs unstable angina stable angina occurs with exertion while unstable angina comes on while the patient is at rest. 1 chronic stable angina pectoris although experts cannot agree on a definition of sap the consensus is that symptoms should be present for at least 2 months and should not vary in severity character or triggering factors. Stable angina is usually triggered by physical activity. Unstable angina is chest pain that occurs at rest or with exertion or stress.
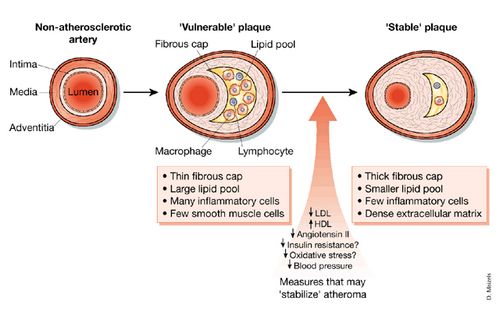
The pain worsens in frequency. Besides physical activity other factors such as emotional stress cold temperatures heavy meals and smoking also can narrow arteries and trigger angina. Any change in the quality frequency or duration of the pain or the precipitating factors suggests unstable angina which requires immediate medical attention. According to the present conception of the pathogenesis ruptures at points of hig.
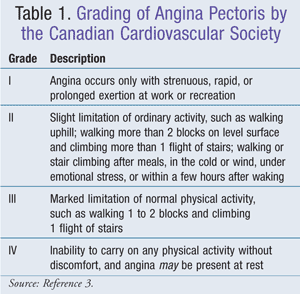
Unstable angina does not follow a pattern. Unstable angina can also occur with or without physical exertion. Possible complications of stable angina include heart attack sudden death caused by abnormal heart rhythms and unstable angina. Stable angina is chest discomfort shortness of breath or any of the symptoms described above that happens with a predictable reliable amount of exertion or stress and when that pattern has been present for more that four weeks.
Although stable and unstable angina have similar symptoms they differ in terms of severity and when the symptoms occur. Stable angina occurs because the blood going to the heart muscle is not enough to cover for the extra workload in exercise. Since unstable angina is not relieved by rest the suspected patient will get started on mona morphine oxygen nitrogen and aspirin. Unstable angina is a clinical syndrome characterized by increased rate and severity of angina pectoris attacks and sometimes but not always accompanied by ecg changes similar to those seen in coronary insufficiency.
When you climb stairs exercise or walk your heart demands more blood but narrowed arteries slow down blood flow. Rest or medicine may not relieve the pain. Unstable angina is a medical emergency since it can progress to a heart attack. It may be new or occur more often and be more severe than stable angina.